-
Australia
Copyright © 2025 Powered by BCI Media Group Pty Ltd
Confirm Submission
Are you sure want to adding all Products to your Library?
Contact Detail
19 Mar 2024 by Dincel
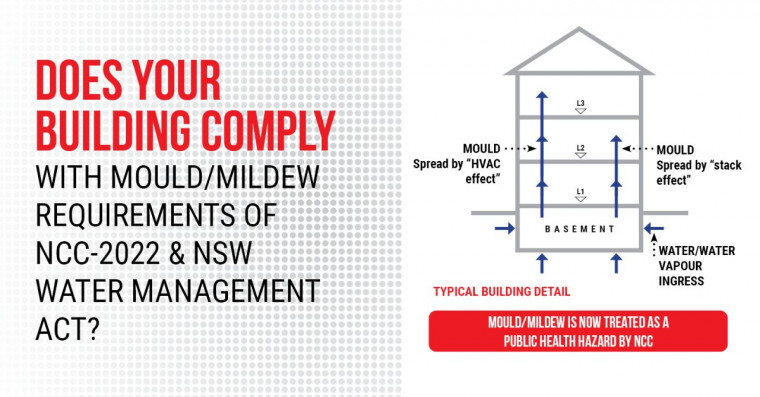
The NCC 2022 Volumes 1 and 2 Performance Requirements F8P1 and H4P7 for Class 1, 2 and 4 states “Risks associated with water vapour and condensation must be managed to minimize their impact on the health of occupants.”
The health of building occupants can be affected if the internal surface of an external (façade and basement) wall demonstrates mould/mildew and fungus development. There are two conditions for these problems to emerge: (a) the presence of water vapour and (b) the availability of nutrients.
Nutrients for growth are unavoidable as spores are always present in the air. They will germinate and grow (even if only at a microscopic level) if temperature and humidity conditions are suitable. Most building materials, furnishings, contents, and the unavoidably dusty environment in the car park/storage area all contain nutrients to some extent. This is beyond the control of the building designer.
Therefore, to avoid mould/mildew and fungus, water and/or water vapour must be eliminated. There are two primary sources causing this problem: (a) condensation related water and (b) leaking external wall. Condensation: Various sources (and academic papers) note that a relative humidity of 60% or greater will provide a condensation water source. So, the humidity level within the interior space and/or the temperature at the internal face of an external wall must be controlled. Leaking external wall: A leaking external wall will result in significantly more water presence than what will occur through a condensation water source, hence all but guaranteeing mould/mildew and fungus development. The NCC 2022 stipulates a DTS requirement to minimize mould/mildew or fungus, or alternatively the Verification Method requires that the mould growth index must be less than 3. Both are very stringent requirements and so the best way to ensure compliance is to design such that no water or water vapour is possible. The main problem with basement walls is water leaks rather than condensation. Any water entering a habitable space in a basement would be unacceptable. Indeed, even water in non-habitable areas of the basement need to be addressed as mould in the basement can impact habitable areas above.Research by the Universities of Yale and Tulsa into mould transmission in a 3-storey building with a single level basement found that up to 30% of the basement mould/mildew travelled to the 2nd floor as shown in the above diagram. The report suggests that mould transmission would be more than 30% for a property with a HVAC System.
Building Designers, Certifiers and Local Councils therefore should consider the following before adopting “Water Shedding Design principles for below ground structures” recently promoted by some industry players:
As explained above, even a small amount of water vapour or water is adequate to cause mould/mildew and fungus growth. Flooding water, unmaintained and/or non-air tight pump out systems, high ground water table, seasonal water table fluctuation, undrained surface rainfall or groundwater seepage, unmaintained/blocked agricultural lines are some of the many reasons for the water source to cause mold/mildew/fungus problem in basements. The only effective solution to prevent water entering the building interior is for the basement to be “fully tanked” or, alternatively, to utilise the DINCEL SOLUTION found at https://www.dincel.com.au/products/waterproof_warranty



